
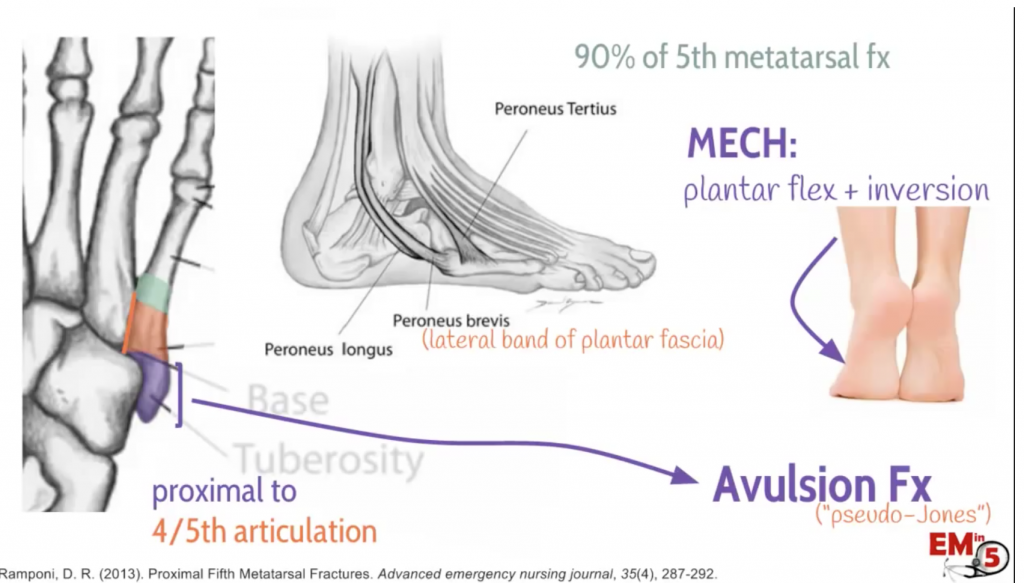
The Ottawa Ankle and Foot Rules should be used to help determine whether radiography is needed when evaluating patients with suspected fractures of the proximal fifth metatarsal.Įarly surgical management of a Jones fracture allows for an earlier return to activity than nonsurgical management and should be strongly considered for athletes or other highly active persons. Nondisplaced tuberosity avulsion fractures can be treated non-operatively. A complete clinical and radiological assessment is required to select the best treatment option. Nondisplaced or minimally displaced (less than 3 mm) fractures of the second to fifth metatarsal shafts with less than 10° of angulation can be treated conservatively with a short leg walking boot, cast shoe, or elastic bandage, with progressive weight bearing as tolerated. Of all foot fractures the fifth metatarsal fracture is the most common. The use of musculoskeletal ultrasonography may be considered to diagnose subtle metatarsal fractures. Lesser toe fractures can be treated with buddy taping and a rigid-sole shoe for four to six weeks. Great toe fractures are treated with a short leg walking boot or cast with toe plate for two to three weeks, then a rigid-sole shoe for an additional three to four weeks. A Jones fracture has a higher risk of nonunion and requires at least six to eight weeks in a short leg non–weight-bearing cast healing time can be as long as 10 to 12 weeks.
Classification of the different forms of fifth metatarsal fracture primarily are. A fifth metatarsal tuberosity avulsion fracture can be treated acutely with a compressive dressing, then the patient can be transitioned to a short leg walking boot for two weeks, with progressive mobility as tolerated after initial immobilization. quency rate as 0.7-1.9 in a combined total of 10,988 foot fractures.lv P.
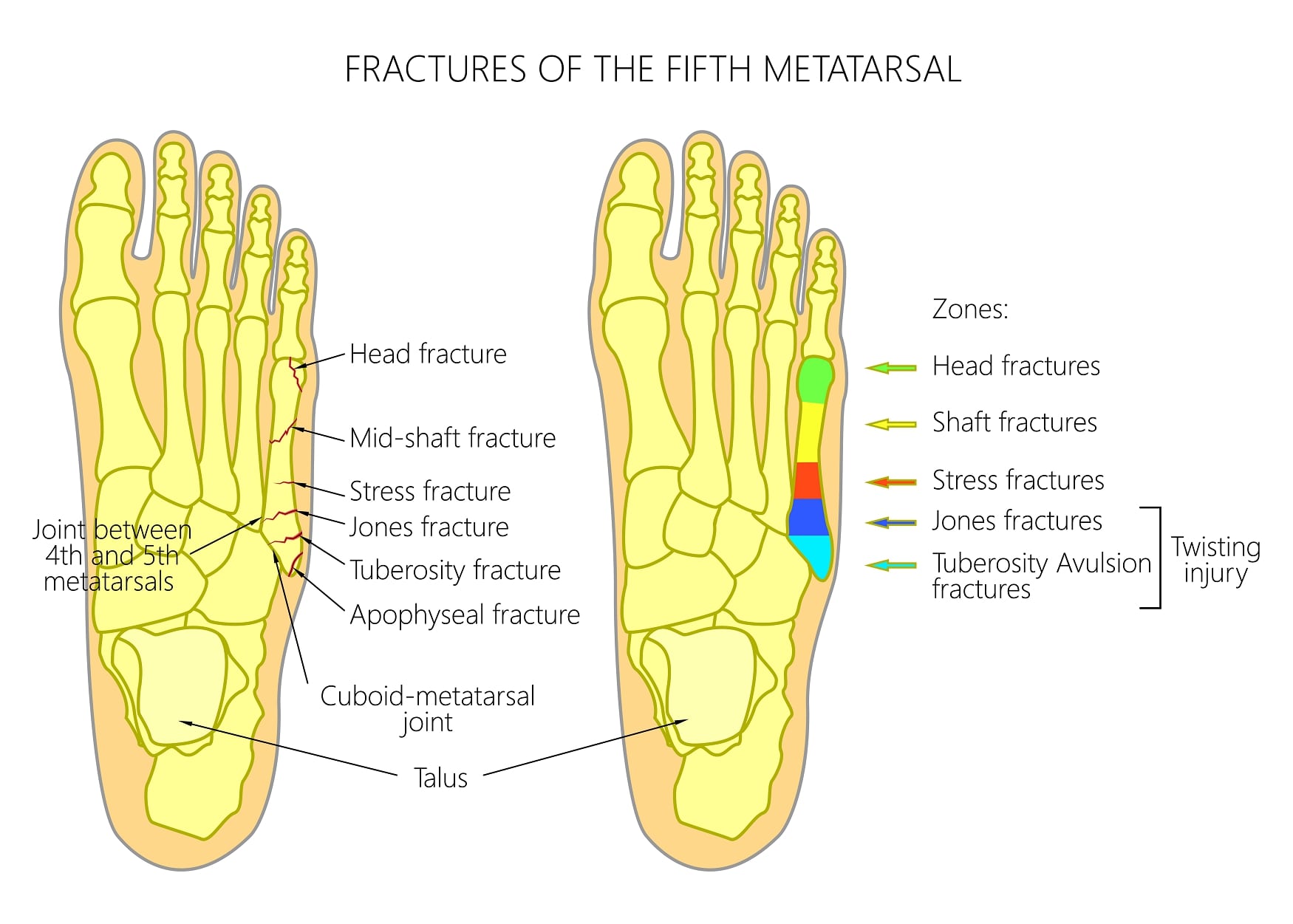
5TH METATARSAL FRACTURE CLASSIFICATION SERIES
However, we have found on reviewing our series of fractures of the base of the fifth metatarsal that most fractures do not fit. Torg divided the fifth metatarsal base into four zones based on common fracture lines. Proximal fifth metatarsal fractures have different treatments depending on the location of the fracture. The most commonly used classification of fifth metatarsal base fractures is the one proposed by Torg et al. Metatarsal shaft fractures are initially treated with a posterior splint and avoidance of weight-bearing activities subsequent treatment consists of a short leg walking cast or boot for four to six weeks. Management is determined by the location of the fracture and its effect on balance and weight bearing.

Diagnosis requires radiographic evaluation, although emerging evidence demonstrates that ultrasonography may be just as accurate. Patients typically present with varying signs and symptoms, the most common being pain and trouble with ambulation. They most often involve the metatarsals and toes. Patients should be informed of the different treatment options and be part of the decision process, especially where time for recovery and returning to previous activities is of essence, such as in the case of high-performance, elite athletes.įifth metatarsal fracture review treatment.Foot fractures are among the most common foot injuries evaluated by primary care physicians. Common surgical complications include hardware failure or irritation of the soft tissues, refracture, non-union, sural nerve injury, and chronic pain.
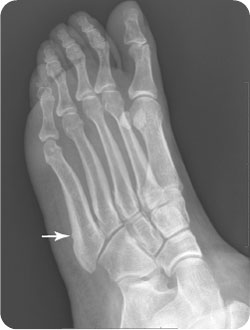
If treated operatively, anatomic reduction and intramedullary fixation with a single screw, with or without biologic augmentation, remains the 'gold standard' of management recent reports however report good outcomes with open reduction and internal fixation with specifically designed plating systems. Small avulsions derived from the tip of the base of the fifth metatarsal may be seen only in the oblique projection of the ankle. Treatment of Zone 2 and 3 fractures remains controversial and should be individualized according to the patient's needs and the 'personality' of the fracture. The 2 most common fractures in the fifth metatarsal are a fracture at the tip of the tuberosity and a transverse fracture 1.5-2 cm from the tuberosity the latter is called a Jones fracture. In the vast majority of patients, Zone 1 fractures are treated non-operatively with good outcomes. Even though fifth metatarsal fractures represent one of the most common injuries of the lower limb, there is no consensus regarding their classification and treatment, while the term 'Jones' fracture has been used inconsistently in the literature.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
